Difference between revisions of "COMP 3000 Essay 2 2010 Question 9"
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
=== The bad === | === The bad === | ||
The main drawback is efficiency. The everlasting memory/efficiency dispute continues as nesting virtualization enters our lives. Furthermore we observed that the paper performs tests at the L2 level, a guest with two hypervisors below it. It might have been useful to understand the limits of nesting if they investgated higher level of nesting such as L4 or L5, just to see what the effect is. | |||
=== The style of paper === | === The style of paper === | ||
Revision as of 20:14, 2 December 2010
Go to discussion for group members confirmation, general talk and paper discussions.
Paper
Authors:
- Muli Ben-Yehuday +
- Michael D. Day ++
- Zvi Dubitzky +
- Michael Factor +
- Nadav Har’El +
- Abel Gordon +
- Anthony Liguori ++
- Orit Wasserman +
- Ben-Ami Yassour +
Research labs:
+ IBM Research – Haifa
++ IBM Linux Technology Center
Website: http://www.usenix.org/events/osdi10/tech/full_papers/Ben-Yehuda.pdf
Video presentation: http://www.usenix.org/multimedia/osdi10ben-yehuda [Note: username and password are required for entry]
Background Concepts
Before we delve into the details of our research paper, its essential that we provide some insight and background to the concepts and notions discussed by the authors.
Virtualization
In essence, virtualization is creating an emulation of the underlying hardware for a guest operating system, program or a process to operate on. [1] Usually referred to as a virtual machine, this emulation usually consists of a guest hypervisor and a virtualized environment, giving the guest operating system the illusion that its running on the bare hardware. But the reality is, we're actually running the virtual machine as an application on the host OS.
The term virtualization has become rather broad, associated with a number of areas where this technology is used like data virtualization, storage virtualization, mobile virtualization and network virtualization. For the purposes and context of our assigned paper, we shall focus our attention on full-virtualization of hardware within the context of operating systems.
Hypervisor
Also referred to as VMM (Virtual machine monitor), is a software module that exists one level above the supervisor and runs directly on the bare hardware to monitor the execution and behaviour of the guest virtual machines. The main task of the hypervior is to provide an emulation of the underlying hardware (CPU, memory, I/O, drivers, etc.) to the guest virtual machines and to take care of the possible issues that may rise due to the interaction of those guests among one another, and with the host hardware and operating system. It also controls host resources. [2]
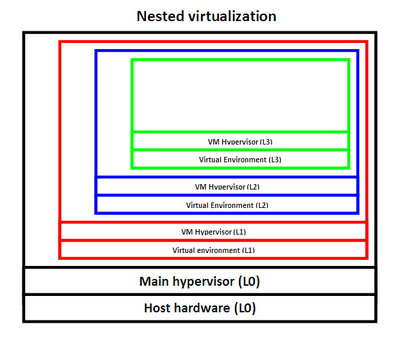
Nested virtualization
The concept of recursively running one virtual machine inside another. For instance, the main operating system hypervisor (L0) runs a VM called L1. In turn, L2 runs another VM L3; L3 then runs L4 and so on (Figure 1). We should also note that we can create multiple virtual machines that exist on the same level, which in turn can have their own nested virtual machines.
Para-virtualization
A virtualization model that requires the guest OS kernel to be modified in order to have some direct access to the host hardware. In contrast to full-virtualization that we discussed in the beginning of the article, para-virtualization does not simulate the entire hardware, it rather relies on a software interface that we must implement in the guest so that it can have some privileged hardware access via special instructions called hypercalls. The advantage here is that we have less environment switches and interaction between the guest and host hypervisors, thus more efficiency. However, portability is an obvious issue, since a system can be para-virtualized to be compatible with only one hypervisor. Another thing to note is that some operating systems such as Windows don't support para-virtualization. [3]
Models of virtualization
Trap and emulate model
A model of virtualization based on the idea that when a guest hypervisor attempts to execute higher level instructions or access privileged hardware components, it triggers a trap or a fault which gets handled or caught by the host hypervisor. Based on the hardware model of virtualization support, the host hypervisor (L0) then determines whether it should handle the trap or whether it should forwards it to the the responsible parent of that guest hypervisor at a higher level.
Protection rings
In modern operating system, there are four levels of access privilge, called Rings, that range from 0 to 3. Ring 0 is the most privilged level, allowing access to the bare hardware components. The operating system kernel must execute at Ring 0 in order to access the hardware and secure control. User programs execute at Ring 3. Ring 1 and Ring 2 are dedciated to device drivers and other operations.
In virtualization, the host hypervisor executes at Ring 0. While the guest virtual machine should normally execute at Ring 3, since its treated as an application, in order to gain privileged hardware access, it triggers a trap that gets handled by the host hypervisor and it eventually end up running in Ring 0.
Models of hardware support
Multiple-level architecture
Every parent hypervisor handles every other hypervisor running on top of it. For instance, assume that L0 (host hypervisor) runs the VM L1. When L1 attempts to execute a privileged instruction and a trap occurs, then the parent of L1, which is L0 in this case, will handle the trap. If L1 runs L2, and L2 attempts to execute privileged instructions as well, then L1 will act as the trap handler. More generally, every parent hypervisor at level Ln will act as a trap handler for its guest VM at level Ln+1. This model is not supported by the x86 based systems that are discussed in our research paper.
Single-level architecture
The model supported by x86 based systems. In this model, everything must go back to the main host hypervisor at the L0 level. For instance, if the host hypervisor (L0) runs L1, when L1 attempts to run its own virtual machine L2, this will trigger a trap that goes down to L0. Then L0 sends the result of the requested instruction back to L1. Generally, a trap at level Ln will be handled by the host hypervisor at level L0 and then the resulting emulated instruction goes back to Ln.
The uses of nested virtualization
Compatibility
A user can run an application thats not compatible with the existing or running OS as a virtual machine. Operating systems could also provide the user a compatibily mode of other operating systems or applications, an example of this is the Windows XP mode thats available in Windows 7, where Windows 7 runs Windows XP as a virtual machine.
Cloud computing
A cloud provider, more fomally referred to as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IAAS) provider, could use nested virtualization to give the ability to customers to host their own preferred user-controlled hypervisors and run their virtual machines on the provider hardware. This way both sides can benefit, the provider can attract customers and the customer can have freedom implementing its system on the host hardware without worrying about compatibility issues.
The most well known example of an IAAS provider is Amazon Web Services (AWS). AWS presents a virtualized platform for other services and web sites to host their API and databases on Amazon's hardware.
Security
We can also use nested virtualization for security purposes. One common example is virtual honeypots. A honeypot is basically a hollow program or network that appears to be functioning to outside users, but in reality, its only there as a security tool to watch or trap hacker attacks. By using nested virtualization, we can create a honeypot of our system as virtual machines and see how our virtual system is being attacked or what kind of features are being exploited. We can take advantage of the fact that those virtual honeypots can easily be controlled, manipulated, destroyed or even restored.
Migration/Transfer of VMs
Nested virtualization can also be used in live migration or transfer of virtual machines in cases of upgrade or disaster recovery. Consider a scenarion where a number of virtual machines must be moved to a new hardware server for upgrade, instead of having to move each VM sepertaely, we can nest those virtual machines and their hypervisors to create one nested entity thats easier to deal with and more manageable. In the last couple of years, virtualization packages such as VMWare and VirtualBox have adapted this notion of live migration and developed their own embedded migration/transfer agents.
Testing
Using virtual machines is convenient for testing, evaluation and bechmarking purposes. Since a virtual machine is essentially a file on the host operating system, if corrupted or damaged, it can easily be removed, recreated or even restored since we can can create a snapshot of the running virtual machine.
Research problem
Rough version. Let me know of any comments/improvements that can be made on the talk page--Mbingham 19:51, 30 November 2010 (UTC)
Nested virtualization has been studied since the mid 1970s (see paper citations 21,22 and 36). Early reasearch in the area assumes that there is hardware support for nested virtualization. Actual implementations of nested virtualization, such as the z/VM hypervisor in the early 1990s, also required architectural support. Other solutions assume the hypervisors and operating systems being virtualized have been modified to be compatabile with nested virtualization. There have also recently been software based solutions (see citation 12), however these solutions suffer from significant performance problems.
The main barrier to having nested virtualization without architectural support is that, as you increase the levels of virtualization, the numer of control switches between different levels of hypervisors increases. A trap in a highly nested virtual machine first goes to the bottom level hypervisor, which can send it up to the second level hypervisor, which can in turn send it up (or back down), until it potentially in the worst case reaches the hypervisor that is one level below the virtual machine itself. The trap instruction can be bounced between different levels of hypervisor, which results in one trap instruction multiplying to many trap instructions.
Generally, solutions that requie architectural support and specialized software for the guest machines are not practically useful because this support does not always exist, such as on x86 processors. Solutions that do not require this suffer from significant performance costs because of how the number of traps expands as nesting depth increases. This paper presents a technique to reconcile the lack of hardware support on available hardware with efficiency. It solves the problem of a single nested trap expanding into many more trap instructions, which allows efficient virtualization without architectural support.
More specifically, virtualization deals with how to share the resources of the computer between multiple guest operating systems. Nested virtualization must share these resources between multiple guest operating systems and guest hypervisors. The authors acknowledge the CPU, memory, and IO devices as the three key resources that they need to share. Combining this, the paper presents a solution to the problem of how to multiplex the CPU, memory, and IO efficiently between multiple virtual operating systems and hypervisors on a system which has no architectural support for nested virtualization.
Contribution
What are the research contribution(s) of this work? Specifically, what are the key research results, and what do they mean? (What was implemented? Why is it any better than what came before?)
The non stop evolution of computers entices intricate designs that are virtualized and harmonious with cloud computing. The paper contributes to this belief by allowing consumers and users to inject machines with their choice of hypervisor/OS combination that provides grounds for security and compatibility. The sophisticated abstractions presented in the paper such as shadow paging and isolation of a single OS resources authorize programmers for further development and ideas which use this infrastructure. For example the paper Accountable Virtual Machines wraps programs around a particular state VM which could most definitely be placed on a separate hypervisor for ideal isolation.
Theory
CPU Virtualization
How does the Nest VMX virtualization work for the turtle project: L0(the lowest most hypervisor) runs L1 with VMCS0->1(virtual machine control structure).The VMCS is the fundamental data structure that hypervisor per pars, describing the virtual machine, which is passed along to the CPU to be executed. L1(also a hypervisor) prepares VMCS1->2 to run its own virtual machine which executes vmlaunch. vmlaunch will trap and L0 will have the handle the tape because L1 is running as a virtual machine do to the fact that L0 is using the architectural mod for a hypervisor. So in order to have multiplexing happen by making L2 run as a virtual machine of L1. So L0 merges VMCS's; VMCS0->1 merges with VMCS1->2 to become VMCS0->2(enabling L0 to run L2 directly). L0 will now launch a L2 which cause it to trap. L0 handles the trap itself or will forward it to L1 depending if it L1 virtual machines responsibility to handle. The way it handles a single L2 exit, L1 need to read and write to the VMCS disable interrupts which wouldn't normally be a problem but because it running in guest mode as a virtual machine all the operation trap leading to a signal high level L2 exit or L3 exit causes many exits(more exits less performance). Problem was corrected by making the single exit fast and reduced frequency of exits with multi-dimensional paging. In the end L1 or L0 base on the trap will finish handling it and resumes L2. this Process is repeated over again contentiously. -csulliva
Memory virtualization
How Multi-dimensional paging work on the turtle project. The main idea with n = 2 nest virtualization there are three logical translations: L2 to Virtual to physical address, from an L2 physical to L1 physical and form a L1 physical to L0 physical address. 3 levels of translations however there is only 2 MMU page table in the Hardware that called EPT; which takes virtual to physical and guest physical to host physical. They compress the 3 translations onto the two tables going from the being to end in 2 hopes instead of 3. This is done by shadow page table for the virtual machine and shadow-on-EPT. The Shadow-on-EPT compress three logical translations to two pages. The EPT tables rarely changer were the guest page table changes frequently. L0 emulates EPT for L1 and it uses EPT0->1 and EPT1->2 to construct EPT0->2. this process results in less Exits.
I/O virtualization
How does I/O virtualization work on the turtle project? There are 3 fundamental way to virtual machine access the I/O, Device emulation(sugerman01), Para-virtualized drivers which know it on a driver(Barham03, Russell08) and Direct device assignment( evasseur04,Yassour08) which results in the best performance. to get the best performance they used a IOMMU for safe DMA bypass. With nested 3X3 options for I/O virtualization they had the many options but they used multi-level device assignment giving L2 guest direct access to L0 devices bypassing both L0 and L1. To do this they had to memory map I/O with program I/0 with DMA with interrupts. the idea with DMA is that each of hiperyzisor L0,L1 need to used a IOMMU to allow its virtual machine to access the device to bypass safety. There is only one plate for IOMMU so L0 need to emulates an IOMMU. then L0 compress the Multiple IOMMU into a single hardware IOMMU page table so that L2 programs the device directly. the Device DMA's are stored into L2 memory space directly
Macro optimizations
How they implement the Micro-Optimizations to make it go faster on the turtle project? The two main places where guest of a nested hypervisor is slower then the same guest running on a baremetal hypervisor are the second transition between L1 to L2 and the exit handling code running on the L1 hypervirsor. Since L1 and L2 are assumed to be unmodified required charges were found in L0 only. They Optimized the transitions between L1 and L2. This involves an exit to L0 and then an entry. In L0 the most time is spent in merging VMC's, so they optimize this by copying data between VMC's if its being modified and they carefully balance full copying versus partial copying and tracking. The VMCS are optimized further by copying multiple VMCS fields at once. Normally by intel's specification read or writes must be performed using vmread and vmwrite instruction (operate on a single field). VMCS data can be accessed without ill side-effects by bypassing vmread and vmwrite and copying multiple fields at once with large memory copies. (might not work on processors other than the ones they have tested).The main cause of this slowdown exit handling are additional exits caused by privileged instructions in the exit-handling code. vmread and vmwrite are used by the hypervisor to change the guest and host specification ( causing L1 exit multiple times while it handles a single l2 exit). By using AMD SVM the guest and host specifications can be read or written to directly using ordinary memory loads and stores( L0 does not intervene while L1 modifies L2 specifications).
Critique
The good
The paper unequivocally demonstrates strong input in the area of virtualization and data sharing within a single machine. It is aimed at programmers and does not affect the end-user in clearly detectable deviation regarding the usage of applications on top this architecture. Nevertheless contribution is visible with respect to security and compatibility. Since this is first successful implementations of this type that does not modify hardware (there have been half efficient designs), we expect to see increased interest in nested integration model described above. The framework makes for convenient testing and debugging due to the fact that hypervisors can function inconspicuously towards other nested hypervisors and VMs without being detected. Moreover the efficiency overhead is reduced to 6-10% per level thanks to optimizations such as ommited vmwrites and direct paging (multi level paging technique) which sounds very appealing.
The bad
The main drawback is efficiency. The everlasting memory/efficiency dispute continues as nesting virtualization enters our lives. Furthermore we observed that the paper performs tests at the L2 level, a guest with two hypervisors below it. It might have been useful to understand the limits of nesting if they investgated higher level of nesting such as L4 or L5, just to see what the effect is.
The style of paper
The paper presents an elaborate description of the concept of nested virtualization in a very specific manner. It does a good job to convey the technical details. Depending on the level of enlightenment towards the background knowledge it appears very complex and personally it required quite some research before my fully delving into the theory of the design. For instance the paragraph 4.1.2 "Impact of Multidimensional paging" attempts to illustrate the technique by an example with terms such as ETP and L1. All in all, the provided video highly in depth increased my awareness in the subject of nested hypervisors.
Conclusion
Bottom line, the research showed in the paper is the first to achieve efficient x86 nested-virtualization without altering the hardware, relying on software-only techniques and mechanisms. They also won the Jay Lepreau best paper award.
References
[1] Tanenbaum, Andrew (2007). Modern Operating Systems (3rd edition), page 569.
[2] Popek & Goldberg (1974). Formal requirements for virtualizable 3rd Generation architecture, section 1: Virtual machine concepts
[3] Tanenbaum, Andrew (2007). Modern Operating Systems (3rd edition), page 574-576.