COMP 3000 2011 Report II:PC-BSD
Part II
Software Packaging
This distribution is PC-BSD. The package formats are the different file formats used to package software for various Unix/Linux distributions. Here in PC-BSD, it mainly uses Binary Packaging format -- pbi<ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_software_package_management_systems#PC-BSD</ref>. This distribution uses lots of graphic utilities<ref>http://www.pcbsd.org/about/pc-bsd-project/utilities</ref> to offer front-end to useful FreeBSD features, such as Software Management Utility, Virtual Environment Utility, Backup Utility, Ports Jails Utility and so on.
In the distribution, it use we can use pkg management utilities<ref>http://wiki.pcbsd.org/index.php/Ports_Jail</ref> to manage packages.In command line, it will use "pkg_info" to get a list of installed packages, "pkg_add" to add packages, and "pkg_delete" to remove packages. In PC-BSD 9.0, it will use PBI manager<ref>http://wiki.pcbsd.org/index.php/PBI_Manager</ref>, which will use "pbi_info", "pbi_add", "pbi_delete" instead. The PC-BSD repository<ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PC-BSD#Package_management</ref> is http://www.pbidir.com/. The software catalog can found from there.
Because PC-BSD provides Graphic tools for desktop user, there is utility Software Management to do some thing like pkg management. Here it is:
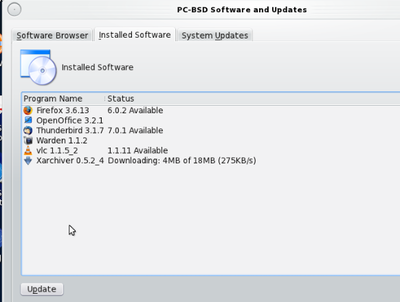
There is utility called Software Management (in PC-BSD version 8.2), which can get a list of installed packages, except for system packages installed during installation of this distribution, like this picture:
PC-BSD is aim to give user easy used install/remove package experience like Windows or Mac OS. The applications are installed from a simple downloaded file with graphic prompts. Software Management is also a very useful utility to find desired software and install them by clicking the link. Remove is also a simply mouse click operation. There is a website browser in the Software Management and search engine for keyword search and different catalogs for selections.
After made decision, it can downloaded the software by clicking the download link. And it will automatically download and install the packages/software.
There is also a remove button under "Installed Software" menu. Simply choose the package needed to remove, and click remove.
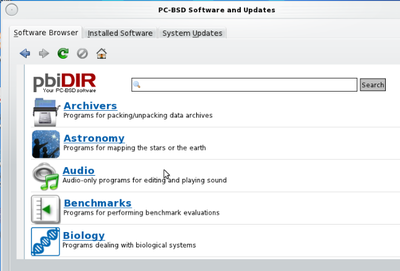
The software catalog for this distribution can be found in the Software Browser of Software Management. There are many selections: Archives, Astronomy, Audio, Benchmarks, Biology, CAD, Communications, Databases, Desktop Utilities, Development, E-Mail, Editors, Educational, Emulators, File Transfer & Utilities, Finance, Games, Graphics, IRC, Japanese, Java, Languages, Math, Miscellaneous, Multimedia, Network-IM, Network-Management, Network-P2P, Network-Utilities, News, Non-Port, Polish, Ports-Management, Print, Science, Security, Shells, System Utilities, Text Processing, The Warden-Inmates, Web, X11, X11-File Managers and X11-Window Managers.
There is too many packages to choose, part of catalog information can be seen from the previous picture.
Major package versions
The package version information can be found by using command "pkg_info". Find the packages and version number and get more information by searching that specific version through Internet. "diff" will compare two binary code line by line. We could use "diff" command to compare two packages, one is downloaded from official website & another one is source from this distribution. After that we can see what's the difference and what has been modified by distribution authors.
X.org:
version number: 11.0, release 7.5 (Oct 26, 2009) <ref>http://www.x.org/wiki/Releases/7.5</ref>. URL:http://www.x.org/wiki/Releases/7.5
latest version: X11R7.6 on Dec 20, 2010.<ref>http://www.x.org/wiki/Releases/7.6</ref>
reason: Xorg supports several mechanisms for supplying/obtaining configuration and run-time parameters: command line options, environment variables, the xorg.conf configuration file, auto-detection, and fallback defaults. In PC-BSD, it completes distribution meta-port.
Qt
version number: 4.7.1, released Nov 9, 2010 <ref>http://labs.qt.nokia.com/2010/11/09/qt-4-7-1-released/</ref> URL: http://qt.nokia.com/downloads
latest version: 4.7.4, released Sep 1, 2011 <ref>http://labs.qt.nokia.com/2011/09/01/qt-4-7-4-released/</ref>
reason: Qt SDK combines the Qt framework with tools designed to streamline the creation of applications for Symbian and Maemo, MeeGo (Nokia N9) in addition to desktop platforms, such as Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. PC-BSD needs that platform.
gtk
version number: 2.22.1, Nov 15, 2010 <ref>http://mail.gnome.org/archives/ftp-release-list/2010-November/msg00145.html</ref> URL: http://ftp.gnome.org/pub/gnome/sources/gtk+/
latest version: 2.24.8, Nov 10, 2011 <ref>http://mail.gnome.org/archives/gtk-devel-list/2011-November/msg00026.html</ref>
reason: Gimp toolkit for X11 GUI. It is is a multi-platform toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces, which is PC-BSD's need.
bash
version number: 4.1.9, March, 2010 <ref>ftp://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/bash/bash-4.1-patches/bash41-009</ref> URL: http://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/bash/
latest version: 4.2.10, April, 2011 <ref>ftp://ftp.cwru.edu/pub/bash/bash-4.2-patches/bash42-010</ref>
reason: The GNU Project's Bourne Again SHell. Bash is the shell, or command language interpreter, that will appear in the GNU operating system.
pth
version number: 2.0.7 Jun 8, 2006 <ref>http://www.gnu.org/s/pth/</ref> URL: http://www.gnu.org/s/pth/
latest version: current is the latest version
reason: Pth is a very portable POSIX/ANSI-C based library for Unix platforms which provides non-preemptive priority-based scheduling for multiple threads of execution inside event-driven applications. PC-BSD want to give user better experience in desktop like Windows or Mac OS, multi-thread is needed.
ruby
version number: 1.8.7 June 1, 2008 <ref>http://www.ruby-lang.org/en/feeds/news.rss</ref> URL: http://www.ruby-lang.org/en/news/2008/05/31/ruby-1-8-7-has-been-released/
latest version: 1.9.3 Oct 30, 2011 <ref>http://www.ruby-lang.org/en/feeds/news.rss</ref>
modification: A dynamic, open source programming language with a focus on simplicity and productivity. Most Unix/Linux distribution will use that, so do PC-BSD. It has an elegant syntax that is natural to read and easy to write.
KDE (this includes Konqueror web browser and KMail)
version number: KDE version 4.5.5, Jan 4, 2011 <ref>http://techbase.kde.org/Schedules/KDE4/4.5_Release_Schedule#January_4th.2C_2011:_Release_KDE_SC_4.5.5</ref> URL: http://kde.org/info/4.5.5.php
latest version: 4.7.3 Nov, 2011 <ref>http://www.kubuntu.org/news/by-date/201111</ref>
reason: KDE offers a full suite of user workspace applications which allow interaction with these operating systems in a modern, graphical user interface. And PC-BSD need good GUI to provide nice experience for desktop user, KDE is a good choice
Gwenview
version number : 1.2.92 Aug 21, 2005 Image viewer for KDE. URL: http://rpmfind.net/linux/RPM/sourceforge/g/project/gw/gwenview/gwenview/1.2.92/gwenview-1.2.92-0.1.101mdk.i586.html
latest version: 4.7.3, Oct 28, 2011 <ref>ftp://ftp.kde.org/pub/kde/stable/latest/src/</ref>
reason: Gwenview is part of the kdegraphics module. Gwenview is a fast and easy to use image viewer/browser for KDE. PC-BSD use KDE for better user experience. Gwenview is inside KDE.
amarok
version number: 2.3.2 Sep 20, 2010 URL: http://amarok.kde.org/en/releases/2.3.2
latest version: 2.5 Beta1, Nov 6, 2011 <ref>http://amarok.kde.org/</ref>
reason: Media Player for KDE4. PC-BSD want to provider service for daily uses, and for desktop user. Multimedia is needed so that a media player like amarok will be a necessary utility.
Initialization
Upon initialization of Pcbsd, the following happens or the following programs run. To access the following program from the terminal, the code used is : cd/usr/local/etc/rc.d. After which the command ls is typed to see the programs that run on initialization, it is from the list that the following programs where chosen, using the code cat "program name"
(cat ffserver) ffserver - is the run after the network service is run, it is a streaming server for both audio and video.
fusefs - is run after systctl is run before mountlate is run, this.
pcbsdinit - Is run after DAEMON is run it starts the system scripts.
gpsd - runs after networking deamon cleanvar devfs is runing and runs before ntpd, it is an interface daemon for GPS receivers.
oss - also runs after deamon, it handles the sound system.
netatalk - runs after daemon, it provides atalkd papd cnid_metad timelord afpd,
snddetect - runs after daemon, it provides sound detect, it first removes sound flag then detects if system has sound or not.
wacom - runs after filesystem, it offers setup and cleanup to configure Xorg for use of the driver or remove the configuration settings.
Reference
<references/>