COMP 3000 2011 Report: ttylinux
Part 1
Background
The distribution I chose is ttylinux, named for its initial orientation towards TeleTYpewriter, or TTY serial interfaces. It caters itself to a target audience that includes both users, looking either to get older hardware up and running on the web or for a lightweight portable system they can boot off a USB stick, and developers who are either looking for an OS they can use on embedded systems or for one to base their own variant of Linux on. It was initially developed in 2001 by Pascal Schmidt, who focused on getting it running on serial interfaces over networks, but when Douglas Jerome took his place in 2008, the focus of the project moved away from connecting to serial interfaces and towards its intended purpose of being "one of the smallest up-to-date Linux systems that is similar to a larger distribution", as stated on its website.
You can download ttylinux on the [project website], or from one of a number of the mirrors it lists. Derived from scratch, ttylinux has a file system that can be as small as ~8 megabytes, making it as little as ~12 megabytes with the kernel; however, the smallest default install for i686 uses ~25 megabytes.
Installation/Startup
Installation
To test this distribution, I used Oracle VM VirtualBox Version 4.1.0r73009 and created a new VM using the Linux 2.6 presets and 2 gigabytes of storage, and configured it to have 16 megabytes of video memory, 64 megabytes ram and a bridged ethernet device to connect directly through my network's router. I then used the virtual media manager in VirtualBox to mount the ~35 megabyte ut-ttylinux-i686-12.6.iso, which is an image of the most recent version of the i686 compatible install, and booted the virtual machine.
The ttylinux installer initially greeted me with some boot options that allowed a number of settings and services available during the installation to be tweaked, and not needing any of these things to be changed, I pressed enter to begin the installation. It loaded into a version of ttylinux that appears to be about the same as it intends the finished install to look like, and you're presented with a shell prompt where I was able to login with the username 'root', and 'password' for the password. The currently out of date [ttylinux User Guide] explains a method of installation that seems to involve a somewhat manual install process, but in the root user's home directory, I discovered a file named 'install.conf' that explained a (relatively) more user friendly way, and I decided to leave the ttylinux User Guide behind in favour of following this.
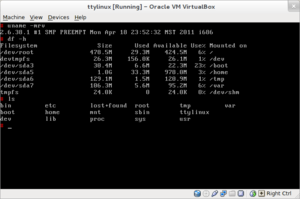
To install ttylinux using 'install.conf', I needed to use fdisk to partition the VM's disk first, and I used a similar configuration to the one in the sample that the default 'install.conf' provides. I then used 'vi' to edit the 'fstab' section in 'install.conf' to reflect the the partitions I created, and to test ttylinux's claim of being up to date, I set the filesystems of everything (except for swap, of course) to ext4, resulting in the following configuration:
/ P /dev/sda1 512M Linux ext4 swap P /dev/sda2 128M Linux Swap swap /boot P /dev/sda3 24M *Bootable Linux ext4 /home E /dev/sda5 1128M Linux ext4 /tmp E /dev/sda6 128M Linux ext4 /var E /dev/sda7 111M Linux ext4
The rest of the configuration was taken care of entirely within 'install.conf', and it involved setting the desired hostname and host address to 'ttylinux' and 127.0.0.1 respectively, the local timezone to 'EST', some basic network configuration to connect to my network using the bridged network adapter I'd created, and some options for the boot loader including where it should be installed. At this point, I ran 'ttylinux-installer --config=install.conf /dev/hdc', meaning that 'ttylinux-installer' would use './install.conf' as the configuration file and that the install cd was /dev/hdc, and it quickly used the configuration I'd set to format the partitions to the filesystems I'd set for them, created a chroot environment using them and installing ttylinux to in the new environment with the settings I'd chosen.
Once the installation was complete, I used VirtualBox's virtual media manager to remove ut-ttylinux-i686-12.6.iso from the VM's virtual cdrom drive, and rebooted into the new system.
- I'd initially tried playing around with an optional section in 'install.conf' that lets you install specific packages rather than the entire system; however, 'ttylinux-installer' kept failing with errors about missing files when I'd attempt to run it this way, and after a few attempts at some more creative solutions to the problem, I realized that I'd needed to use a full install when I discovered that the files the installer was looking for were in the few packages I'd been comfortable setting it to skip.
Startup
Booting the VM for the first time after installing ttylinux, I was presented with a creatively themed lilo bootloader with a single option to start ttylinux that it selected automatically after a brief countdown. The installed ttylinux system loaded very similar to the install when it booted up, the only major difference I noticed as the text whipped by being that it also checked and mounted the partitions I'd defined in 'install.conf'. Once it had finished loading, I logged in with the same credentials as I had in the installer before promptly using 'passwd' to give the root user a more secure password, and then used 'vi' to edit '/etc/issue' and '/etc/issue.tty' to remove the line that explained the default username and password above each login prompt.
I quickly discovered that I couldn't seem to access the web, and when I checked 'ifconfig' to see that I appeared to have a functional network connection, I used my host OS to find the ip associated with 'www.google.com' and found that my VM was able to ping that, which meant that the problem was likely with '/etc/resolv.conf'. Sure enough, when I checked to see what was wrong with '/etc/resolv.conf' I found that it didn't exist, and after running the command "# echo 'nameserver 192.168.0.1' > /etc/resolv.conf" to create a new one that would use my router's local address to lookup URLs, I tried pinging 'www.google.com' and found that my problem had been fixed.
Everything seemed to be working at this point, and I decided to play around with the system to see what it was like...
Basic Operation
As I stated earlier, the intended purpose of ttylinux is to "make one of the smallest up-to-date Linux systems that is similar to a larger distribution", and while it is small, I decided to take a look at what it was made of to see just how up to date and similar to a larger distribution it was...
I began by taking a look around the file system to see what makes ttylinux tick, and noticed that the '/dev' folder uses udev to manage devices just like nearly all modern distributions of linux; I changed 'SYMLINK+="cdrom"' in '/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-cd.rules' to SYMLINK+="ccdrom"' to see whether rules would work, and sure enough, the link to the cdrom device '/dev/ccdrom' existed in place of '/dev/cdrom' when udev was restarted.
Being up to date means being able to do essential tasks over networks too, so I attempted to download a file with wget, use scp to copy a file to a remote server and log into a remote host using ssh to see if it met those basic networking requirements, and I was pleased to find myself successful in each case. When I noticed ttylinux has ncurses, I immediately hoped there'd have been an ncurses web browser like 'lynks' or 'links' available too, but had no such luck.
Curious how system services worked in ttylinux, I took a look and found that the files in /etc/sysconfig/ each allow for disabling or enabling a service on boot with a variable set to 'yes' or 'no', while some of them also include a variable containing command-line arguments as well. A combination of the 'rc.*' files in '/etc/rc.d/' then appear to be hard-coded to read the values of these variables and decide which services to start and what arguments to give them when they are.
There isn't a huge amount to do in ttylinux beyond basic command-line functionality, but its interesting to explore the system and see how it works from the point of view of porting it to a more specific purpose, and I didn't end up having any problems once I was up and running.
Usage Evaluation
To see if ttylinux would really live up to its name, I ran the command "# du -c -m /" and was impressed to find that the full i686 install only took up ~25 megabytes. The ttylinux [project website] reports on its front page that it "has an 8 MB file system and runs on i486 computers within 28 MB of RAM, but provides a complete command line environment and is ready for internet access", but digging a bit deeper I found that this is only true for the statically linked 'sm' version with a static '/dev' environment, and that the 'ut' version that I installed that uses 'udev' is reported to have a 24 megabyte filesystem just like mine reported having.
I soon found myself missing programs like 'file', 'man', 'gpasswd' and 'tree', which I'd previously considered being core set of utilities in any Linux distribution. I was also sad to see 'vim' missing, and discovered how much it really is an improvement over 'vi', which turns out to have a vastly reduced feature set in comparison, and also appearing to lack a proper implementation for using arrow keys, meaning that changing lines without returning to normal mode is frustrating at best. That said however, there is a decent array of functionality packed in those ~25 megabytes too, including a set of unix utilities provided by busybox and a nice collection of other utilities I wouldn't have inherently expected like 'adduser', 'wget' and 'fuser'. There are also [add-ons] available to provide support for ntfs, the calc utility and an http server, and a [source distribution] exists that includes a build system if additional functionality is required.
Pleased by the use udev, I was equally concerned by ttylinux's choice to use inetd rather than the much more commonly used xinetd to manage network services, and can only assume the choice to use it, which sacrificed the goal to be up-to-date and similar to a larger distributions, would have been made in favour of the main goal of keeping the size down. Otherwise, I'd have to consider this a flaw in ttylinux's implementation.
Being minimalistic by design to meet its goal of being the smallest modern Linux distribution, I can't really fault ttylinux for what its missing, and it does make an attempt at providing users with the ability to include additional functionality they might need themselves, albeit not in the easiest manner; therefore, I think my only complaint in that respect would have to be the lack of basic gcc/make package for users who might want to take ttylinux a bit further without needing to use the source distribution (or the much larger 'ws' version, which doesn't currently seem to be available). Otherwise, assuming inetd is used to keep the size down, ttylinux does what it says and seems to do it well once its installed, and the only other critique I can make from what I've seen, is for including the package selection feature in the ttylinux-installer script when it's clearly not yet stable.
References
"ttylinux homepage." Minimal Linux. Web. 19 Oct. 2011. <http://www.minimalinux.org/ttylinux/>