BioSec 2012: Cheryl
Trying to tie Computer Security into all of this
Using Darwin’s approach
- Really slow: it took biology billions of years to get to the efficiency it now is at. How are we supposed to compete with that?
- If we follow the same process we are setting up for failure most of the time…species getting extinct because they failed most of the time
- Species survival is highly dependent on environment…computer security needs to basically work all the time independent of its environment …how is this going to work?
So for things to work:
- there needs be a lot of redundant stuff:
- Genes – redundant ways to get an amino acid
- Genome – copies of the same genes
- Pathways – many regulators
- diversity
- Biology is so good because there aren’t two things that are really the same…they have a lot in common…but there is that one small aspect that sets them apart…if they were all the same then one small thing just wipes all of them out
- Can this be done with computers…randomize things by adding introns (junk code)?
Textbook Notes
Chapter 1: Light and Life==
- Light
- source of information and energy
- Defined as EM radiation
- Wave of photons
- Can be absorbed by pigments and then used
- Colour = light that is not absorbed by pigment
- Electrons become excited when absorbed by light which in turn then becomes potential energy (photosynthesis)
- Photoreceptor
- light-sensing system
- made up of pigment molecule bound to protein
- eye = organ of animals to sense light
- Problem:
- most light driven processes can only process a certain part of the EM spectrum
- source of energy…too much can cause deadly effects
- pigment melanin in our skin absorbs UV (high energy and can be damaging)
- Circadian rhythms (body clock) the daily cycle of most living organisms have evolved to adapt to the change in light (night and day…plant use photosynthesis during the day and night break glucose)
- Some animals prefer the dark (nocturnal animals like moths)
- Some animals have ancestors that had functional eyes but are not blind (blind mole rat)
- bioluminescent: organisms that use chemical energy to make their own light to attract a mate, camouflage, attract prey or communicate
Chapter 2: Origins of Life
- life defined by seven characteristics:
- Display order: high ordered structures
- Harness and utilize energy: getting and using chemical energy to power the organism’s activities
- Reproduce: ability to reproduce their own kind
- Respond to stimuli: ability to respond environmental stimuli
- Exhibit homeostasis: ability to control an organism’s internal environment within the limits to sustain life
- Growth and development: consistent growth and development (DNA inheritance)
- Evolve: adapt to environments over many generations to have better reproducibility and survival of the species.
- Cell theory
- All living organisms are composed of cells
- Cells are the functional units of life
- New cells come only from preexisting cells (division)
- Eukaryotic Cells
| Function | Organelles/Structures involved |
|---|---|
| Genetic control of the cell | Nucleus and ribosomes |
| Manufacture, distribution, and breakdown of molecules. | Endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and peroxisomes |
| Energy processing | Mitochondria (plus chloroplasts in plant cells) |
| Structural support, movement, and communication between cells | Structural support, movement, and communication between cells |
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved by endosymbiosis which suggests mitochondria and chloroplasts were small prokaryotes and they began living within larger cells
- Cytoskeleton:
- network of protein fibers in the cells
- functions in structural support and mobility
- interacts with motor proteins resulting in mobility and cellular respiration
- composed of three kinds of fibers:
- Microfilaments: (actin filaments) support the cell’s shape and are involved in mobility
- Intermediated filaments: (not present in plant cells) reinforces the cell shape and provides and anchor for the organelles
- Microtubules: (made from tubulin) responsible for cell rigidity and guiding the organelle’s movement
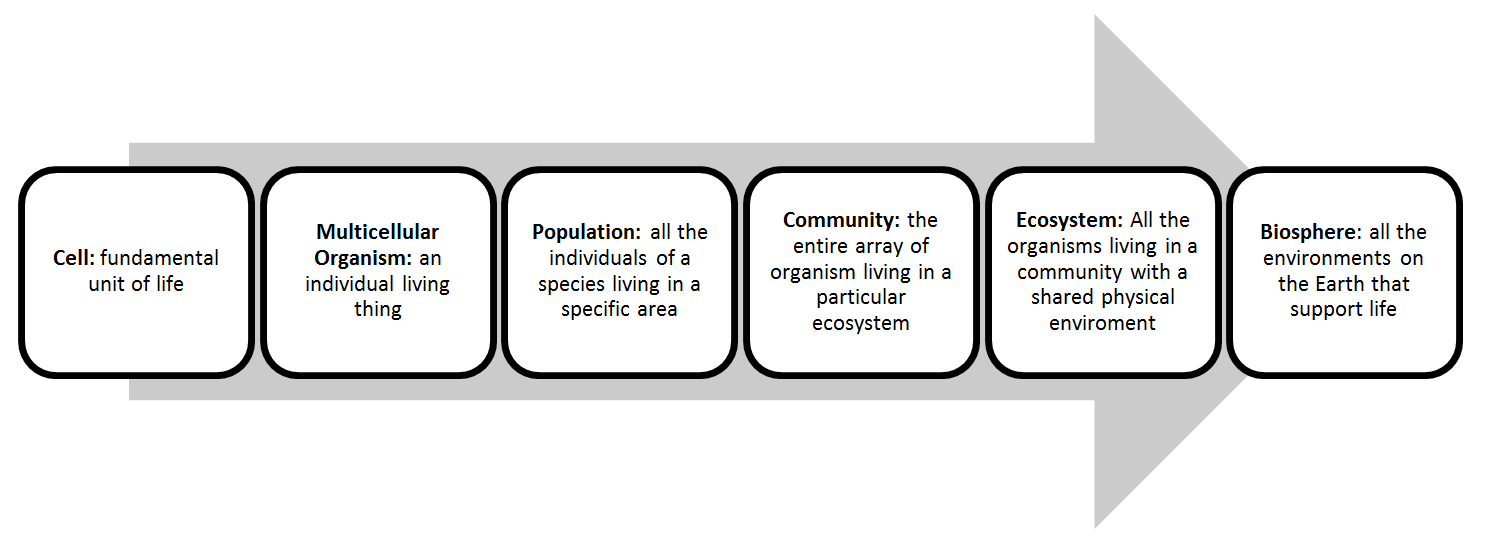
Chapter 3: Selection, Biodiversity and Biosphere
- Biological organization:
- Categorizing organisms on how they obtain carbon
- Autotrophs: create their energy-containing organic carbon molecules (glucose) from inorganic carbon molecules (sunlight). Example: plants using photosynthesis
- Heterotrophs: get energy-containing organic carbon molecules (glucose) by consuming other organisms. Example: animals eating plants or other animals.
- Categorizing organisms on how they obtain energy
- Phototrophs: obtain energy from light
- Chemotrophs: obtains energy by oxidizing inorganic or organic substances
- Theory of evolution: all organisms descended from one common ancestor, thus share common features. At the same time due to natural selection species change over time to adapt to their specific environment
- All living organisms have three essential components:
- ATP for energy
- DNA for genetics
- Plasma membrane
- Parasitism = symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits at the expense of the other
- Mutualism = symbiotic relationship where both organism benefit
- Interesting: The genetic barcode that is embedded in almost every cell is the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase 1
Computer security aspect
- diversity
- Biology is so good because there aren’t two things that are really the same…they have a lot in common…but there is that one small aspect that sets them apart…if they were all the same then one small thing just wipes all of them out
- Can this be done with computers…randomize things by adding introns (junk code)?
Chapter 4: Energy and Enzymes
- Cells can be basically thought of as a chemical factory (millions of chemical reaction take place in a cell)