COMP 3000 2011 Report: DoudouLinux
Part 1
Background
"Doudou" is a french word for the teddy bear, or blanket, that children love to carry around and hug. In that context, DoudouLinux is a GNU/Linux distribution designed for young children aged from two to seven.<ref name = "DoudouLinux: You know, for kids">Linux info from the source (Last accessed October 17, 2011).</ref>
It is a system that aims at teaching the rudiments of computer use to young children while making it as easy and pleasant as possible for children. Founded by the French Jean-Michel Philippe, it's first release “Gondwana” was released in June 2011 and is based on a minimal Debian “Lenny” linux system.
DoudouLinux is officially available in 25 languages<ref name = "DistroWatch">DistroWatch (Last accessed October 17, 2011).</ref> and can be downloaded it on the DoudouLinux homepage as an ISO image file of approximately 693 MB in size.
Installation/Startup
Installation
The minimum requirements to run DoudouLinux are:<ref name = "Requierements">Downloads (Last accessed October 18, 2011).</ref>
- 256 MB memory
- 800 MHz processor
- 800×600 dots display
I used VMWare Workstation and allocated 8GB for the virtual machine and 512MB of RAM.
During the boot,the choice of booting with or without having persistence is offered.<ref name = "Data Persistence">http://doudoulinux.org/web/english/documentation-7/advanced-tools/article/data-persistence.html Data Persistence] (Last accessed December 15, 2011).</ref>Data persistence consist in loading up the configuration and other programs from a previous use of DoudouLinux. We chose to boot up without persistence.
The installation lasts around thirty seconds and used 1.1 MB of the allocated space on the virtual machine( even though the virtual file folder was took 532 MB of the host disk space). [Figure 1]
No problems were encountered since there is no system configuration or management options and the system does not request setting up a username and password.
Startup
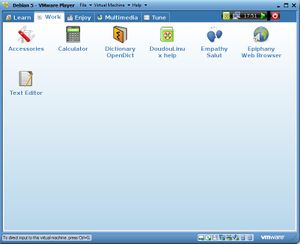
At boot time,there is an "Activities Menu" displayed that offers seven session options: [Figure 2]
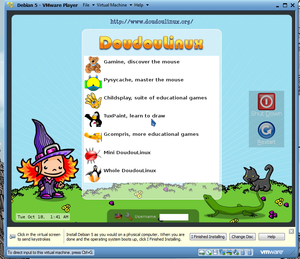
- Gamine
- Pysycache
- Childsplay
- TuxPaint
- GCompris
- Mini DoudouLinux
- Whole DoudouLinux
The first five options are single applications sessions while Mini DoudouLinux is a session with a reduced set of applications offered.
The Whole DoudouLinux option was choosen.
Basic Operation
 |
 |
 |
As shown in the activities menu(Figure 2) the applications are ordered by increasing difficulty.From the two year old child who discovers the mouse and the keyboard(Gamine and Pysycache) to more experienced users with educational suites such as Childsplay and GCompris.
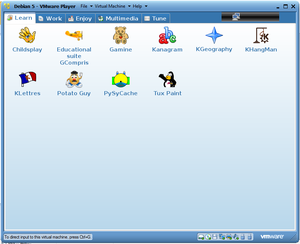
In the Whole DoudouLinux session,close to fifty applications are offered and they are grouped in categories,by type(i.e Work,Learn,Enjoy) that have their own tab in DoudouLinux application Launcher.[Figure 4]
The general games category includes standard puzzle and non-violent arcade fare, plus some common card and board games.
Hours were spent playing the games from the Enjoy category.
.
Usage Evaluation
The DoudouLinux design goals are, in my view, met and exceeded.The system runs fast since there is less configuration to do.The icons are very colorful,suggestive and large enough for children.
Depending on the age of the child,the mouse speed can be easily adjusted as well as the sound output.
In some applications,hovering the mouse on an item provides sound instruction.
The system contain plenty of interactive and tactile-experice tools that respond to single-clicks for better ease-of-use. Since window management would,presumably, be tricky with young children,all the applications or game run in full-screen mode.
.
Part 2
Software Packaging
Packaging Format and Utilities
As Doudoulinux is Debian based,It uses the same package format.deb with the main Debian package management program, dpkg. Since DoudouLinux is based on a minimal Debian “Lenny” Linux system and is geared toward childrens,there is no need for the higher level package management tools such as aptitude or the graphical package manager Synaptic.However,the Advanced Packaging Tool (APT) that relies on dpkg, is installed as well as the utilities for manipulating .deb files: dpkg-deb and dpkg-split.
Listing Installed Packages
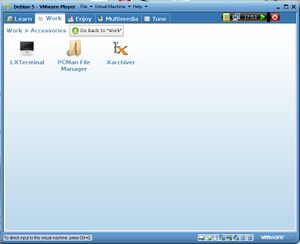
As mentioned above,there are no graphical package manager,such as Synaptic, installed so the only way to get a list of the installed packages is through the terminal.Accessing the terminal isn't obvious since DoudouLinux tries to hide that aspect from children.One has to go to the "Work" tab [Figure 5]and then the "Accessories" tab[Figure 6]. From the command line, you get the list of the packages by typing "dpkg --list".
Adding and Removing Packages
DoudouLinux does not have many packages(~913 packages) compared to other Debian based distributions.The installed packages are those that are required and necessary for the proper functioning of the system.The larger applications present, such as Gamine, are installed for their educational and entertaining value to children.As such there is no Office suite since it is not indispensable for children.
<ref name = "DoudouLinux User Manual ">DoudouLinux User manual (Last accessed November 12, 2011).</ref>
However,a package can be installed,when in superuser, using 'dpkg --install <packageName>.deb' where the packageName is a file in your current working directory. They can be removed by using 'sudo dpkg --remove <packageName>' ,which will leave the package's configuration file, or 'dpkg --purge <packageName>',which will remove the package's configuration file as well.
This method is somewhat inconvenient for adding packages since they must first be downloaded.
A better method is using APT which expands the functionality of dpkg by searching, fetching and installing packages from online repositories along with their dependencies, either from binary files or by compiling source code.<ref name = "Advanced Packaging Tool ">Advanced Packaging Tool (Last accessed November 11, 2011).</ref>
So,in the terminal, typing 'sudo apt-get install <packageName>' will install a particular package along with all of its dependencies, while 'apt-get remove <packageName>' will remove the package<ref name = "The Debian Package Management Tools ">The Debian Package Management Tools (Last accessed November 13, 2011).</ref>
Software Catalog
As mentioned above,DoudouLinux does not have an extensive list of packages that are installed.
Major package versions
Here are the version numbers and upstream sources of various major software packages included in DoudouLinux as part of the standard install, and packages that are central to the system. Notable inclusion in this list are the major applications such as Gamine and Childsplay.
| Package | Version | Upstream Source |
|---|---|---|
| Linux Kernel | 2.6.26-2-686 | http://www.kernel.org/ |
| libc | 2.7-18lenny7 | http://www.gnu.org/s/libc/ |
| X.org X Server | 1.7.3+20 | http://www.x.org/wiki/ (Debian-specific version: http://wiki.debian.org/XStrikeForce) |
| GTK+ | 2.12.12-1 | http://www.gtk.org/ |
| Qt 4 | 4.4.3-1+lenny1 | http://qt.nokia.com/ |
| Bash(The GNU Bourne Again SHell) | 3.2-4 | http://www.gnu.org/software/bash/ |
| Dash | 0.5.4-12 | http://gondor.apana.org.au/~herbert/dash/ |
| Coreutils (GNU core utilities) | 6.10-6 | http://www.gnu.org/s/coreutils/ |
| Busybox | 1.10.2-2 | http://busybox.net/ |
| Epiphany Browser | 2.22.3-9 | http://projects.gnome.org/epiphany/ |
| Openbox | 3.4.7.2-3 | http://openbox.org/ |
| Childsplay | 0.85.1-1.1 | http://www.schoolsplay.org/ |
| Gamine | 1.1-2 | https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/gamine |
| GCompris | 8.4.4-1.1 | http://gcompris.net/-Download- |
| Pysycache | 3.1-2doudou1 | http://www.pysycache.org/web/en/telechargement2.html |
Comparison of Packages to their Latest Stable Release
A disclaimer here is that it was difficult to figure out if the packages had been modified by the distribution authors since finding the actual packages,instead of the binaries, that are installed in the distribution was hard.
Linux Kernel
The Linux Kernel included in DoudouLinux is version 2.6.26-2-686 and was released on August 6,2008.
<ref name = "DoudouLinux Kernel version ">DoudouLinux kernel version (Last accessed November 13, 2011).</ref>
That is pretty old compared to the latest stable version 3.1.1 that was released on November 11,2011.<ref name = "Latest Kernel version ">Latest kernel version (Last accessed November 13, 2011).</ref>
Using the Meld tool,<ref name = "Meld ">Meld (Last accessed November 13, 2011).</ref> which does folder and file comparison, it was obvious that the kernel package hasn't been modified by the DoudouLinux authors since their main goal was to provide the proper GUI and applications to open a child's mind to computer.And it's inclusion is required for the system to be operational.
Libc
DoudouLinux includes version 2.7-18lenny7 of glibc which is a fork of the main branch made by Debian developers for the Debian "Lenny" . It was released on January 22, 2011 <ref name = "Glibc version ">GLibc Publishing history (Last accessed November 15, 2011).</ref>and was the latest stable release of this fork. The latest stable release of libc proper is 2.14 which was released on June 1, 2011. It has not been modified at all for DoudouLinux, and is included as it is the same version of libc that is included in Debian 5 "Lenny". It contains the standard libraries that are used by nearly all the programs on the system.
Bash
DoudouLinux includes version 3.2-4 of Bash which was released on October 11, 2006 <ref name = "Bash version ">Bash Archives (Last accessed November 15, 2011).</ref> . Bash proper latest release is 4.2 which was released on February 13, 2011. <ref name = "Bash wiki ">Bash wikipedia (Last accessed November 15, 2011).</ref> It's inclusion in the DoudouLinux is required .
Coreutils
DoudouLinux includes the version 6.10-6 of Coreutils which is a fork made by the Debian team. It was released on October 29, 2008<ref name = "coreutils">Coreutils Archives (Last accessed November 15, 2011).</ref> The latest stable release of the Debian fork is 8.5-1, but the official stable release of Coreutils is at 8.14 which was released October 12, 2011.<ref name ="GNU Core Utilties.">Gnu Core Utilities (Last accessed November 15, 2011).</ref> It's included as it is required and is the same version that is included in Debian 5 "Lenny" since it contains the essential basic system utilities.
Epiphany Browser
DoudouLinux web browser is Epiphany which is a a simple and intuitive browser aimed at non-technical users and has parental control already set.The distribution version is 2.22.3-9 and was released on June 30,2008<ref name = "Epiphany">Epiphany Archives(Last accessed November 15, 2011)</ref> while the latest stable version is 3.0 and was released on April 5,2011. <ref name = "Epiphany 3.0">Epiphany 3.0(Last accessed November 15, 2011)</ref>
Gamine
Gamine is include in DoudouLinux for its educational value to the two year old who is discovering the mouse.The current version is 1.1-2 and was released in March 15,2011.This is to my knowledge the latest version of Gamine.
GCompris
package name: gcomprise
written in: C and pythong
installed version in our system: 8.4.4-1.1 (found by dpkg -p GCompris)
latest version: 9.6.1-0 (found from ubuntu software repository)
changes made: -- inclusion/exclusion of educational games.
Initialization
we found about initialization of our distribution by following steps.<ref name = "An introduction to services, runlevels, and rc.d scripts ">An introduction to services, runlevels, and rc.d scripts (Last accessed November 16, 2011).</ref>
1. in terminal type (more /etc/inittab) to find out the runlevel.
2. after figuring out the runlevel, we typed ( ls /etc/rc2.d) which has symbolic links to the actual process in inid.d.
following are the symbolic links in rc2.d which maps to process in init.d except readme file.
README
| S01doudou-users S05loadcpufreq |
S14avahi-daemon S19cpufrequtils |
S30gdm S89anacron |
3. then typed (ls /etc/init.d) which lists all start-up scripts.
The ones in bold are maped to the symbolic links in the rc2.d
| acpid acpi-support |
fuse gdm |
loadcpufreq module-init-tools |
rc.local rcS |
4. from there, we could map symbolic links in rc2.d to scripts in init.d.
5. the order was found by going in rc2.d and checking the numbers associated with each symbolic links. we dont know why the numbers are not consecutive but atleast its in increasing order.
Part 3
Comin soon to a Wiki close to you....
References
<references />