DistOS-2011W Akamai and CDN: Difference between revisions
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
=Evaluated Systems/Programs= | =Evaluated Systems/Programs= | ||
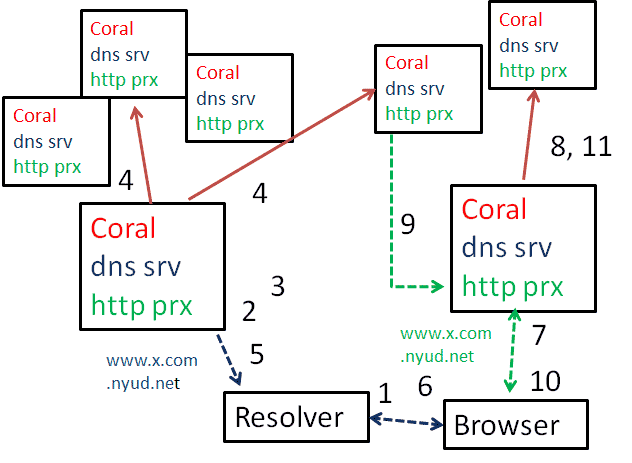
[[File:coral-flow.gif]] | |||
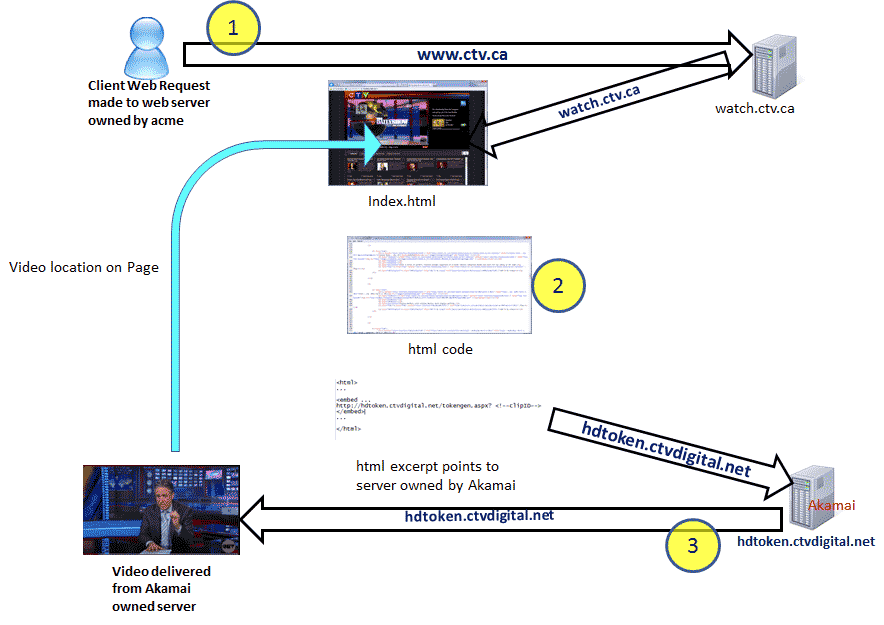
[[File:akamai-flow.gif]] | |||
=Experiences/Comparison (multiple sections)= | =Experiences/Comparison (multiple sections)= | ||
Revision as of 09:19, 5 March 2011
Fahim Rahman
Introduction
Content Distribution Networks (CDN) have increased their position as a vital distributed system to enhance the use of the internet, as applications and media streaming increase in demand with time. A CDN is a distributed system of computers containing copies of data at various points within a network. This aids in maximizing bandwidth for users to access data from different points within the network. The issue of latency is relieved in terms of how an application or data transfer behaves, as the position of these servers tends to be closer to any group of individual users. At its simplest makeup, a CDN is a mirroring mechanism solving part of the last mile issue to ensure a positive user experience when it comes to streaming media or using a web-based application.
Content and associated applications are dictated on the internet by the cost shouldered by the publisher. An individual publisher, or service provider, can reach a large audience by having the funding to administer the combination of load-balanced servers and fast network connections. This can be a significant barrier to entry for a smaller, unfunded service provider. Popularity and trends on the internet can be measured in a wave formation. A small website can experience something referred to as the “Slashdot” effect, where a certain website will experience a load of traffic all at once, as the wave of popularity comes in. Given that many small-time providers of content are not prepared for this kind of popularity, an unintended downtime will be experienced. The levels of traffic are simply unsustainable to the smaller provider. A plausible solution for this issue lies within a content distribution network.
Mirroring has presented itself as a natural solution to provide static content. This requires a voluntary effort with people using their own servers and networks to lend a hand to a provider perceived with value that they want to support. Peer to peer networks and file sharing also displays the effort individual users are willing to put forth to distribute this valued content. The sustainability of this effort is questionable given that it requires on the value proposition to be high enough among a user base with resources to spare. This paper will explore in detail two specific content distribution mechanisms; Coral-CDN, a publicly available resource and Akamai Technologies, a commercial solution. Many other CDNs are available out there, but these two solutions will be explored in detail. To be revealed will be their general approach (section 2), their technical approach (section 3), and the user experience (section 4). A discussion will follow, highlighting issues that each solution experiences and needs to consider for the future (section 5) as well as a conclusion on the CDN space as it relates to the use of the internet (section 6).
Systems/Programs in the Space
Give an overview of the area you are examining. What systems/programs are out there?
Evaluated Systems/Programs
Experiences/Comparison (multiple sections)
In multiple sections, describe what you learned.
Discussion
What was interesting? What was surprising? Here you can go out on tangents relating to your work
Conclusion
Summarize the report, point to future work.
References
Globally distributed content delivery (Akamai) - Accessed Feb. 10, 2011
Coral-CDN paper - Accessed Feb. 18, 2011
The Slashdot Effect (Wikipedia) - Accessed Feb. 24, 2011
Akamai - Why the Edge? - Accessed Feb. 25, 2011
How to build your own CDN... - Accessed Feb 24, 2011
The Design of CoralCDN - Accessed Feb 27, 2011
Akamai - State of the Internet - Accessed January 25, 2011
Akamai - Online Video Publishers - Accessed February 28, 2011