WebFund 2013F Lecture 7: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
** a program calling another and passing stuff around | ** a program calling another and passing stuff around | ||
** ie. like buttons on webpages | ** ie. like buttons on webpages | ||
* [[File: | * [[File:sept30.jpg]] | ||
* block | * block | ||
** running (on a 4 core processor you could have 4 processes running simultaneously) | ** running (on a 4 core processor you could have 4 processes running simultaneously) | ||
Latest revision as of 16:31, 10 November 2013
Audio from the lecture given on September 30, 2013 is available here.
Note
September 30
- cookies
- text document
- saves info on what you were doing on site
- stateless
- HTTPS
- SSH
- what can server do to keep track of client?
- Cookies!
- Something the server sets
- sent along later
- Encode information in the url itself
- that will say what this session identifier is
- Cookies!
- Server can't trust anything the client sends
- webrequests are stateless
- How to make sure the user doesn't mess with your cookies
- have to be encoded
- cookies should look like garbage
- if you can hand edit the cookie you are doing something really dumb
- have to be encoded
- state is being passed around in url
- remote procedure calls
- a program calling another and passing stuff around
- ie. like buttons on webpages
- block
- running (on a 4 core processor you could have 4 processes running simultaneously)
- ready (waiting for a free processor)
- waiting on I/O (blocked until something has happened)
- synchonous I/O
- read (b)
- what happens here?
- Program went to sleep and is woken up
- could be doing other things here instead of giving up the CPU!
- Not efficient to switch between processes
- scanf(b)
- only makes sense after read is completed
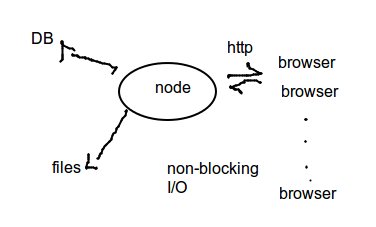
- in node when you do any I/O code it returns immediately
- asynchronous
- callbacks solve asynchronous promblem
- read(s, b, callback)
- do the read request, and when it's done, here is the code to run encoded in this callback
- read(s, b, callback)
- node acts like a dispatcher
- constantly routing data
- classic callback in node
- listen line
- has a port number + callback function
- listen line